Auxin
is a plant growth hormone, its major function is to help the plant grow by
changing the plant wall plasticity making it easier for the plant to grow
upward. Auxin also helps the root formation. Auxin is also the hormone
responsible for phototropism, the process by which auxin is degraded on the
outside of the plant, allowing the plants to slope towards the light. Auxin is also
credited for growing quickly the plants central shaft, which is also known as apical
dominance.
| http://preuniversity.grkraj.org/html/6_PLANT_GROWTH_AND_DEVELOPMENT.htm |
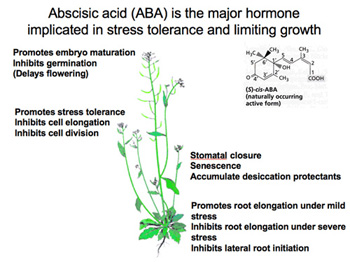
Abscisic
acid (ABA) is produced to counter stress of environmental conditions such as
dehydration, cold temperatures, and shortening day lengths. ABA counters the
effect of hormones like auxins and inhibits stem elongation and induces
dormancy in lateral buds. Abscisic acid also allows the plants to adapt to the
stress in the environment. ABA blocks germination in buds and promotes storage
of proteins, it protects young plants from sprouting too early during warm
weather in winter.
 |
| https://labs.mcdb.ucsb.edu/finkelstein/ruth/ |
Ethylene
is associated with fruit ripening, flower wilting, and leaf fall. It is also a
volatile gas (C2H4). It is a growth hormone that helps
convert starch and acids to sugars. Ethylene also triggers leaf and fruit
abscission.
| http://isopaninsulation.com/technologies/fruit-ripening-plants |
No comments:
Post a Comment